Hydrogen Separation Membrane Research
Main Activities
- Synthesis, processing, and characterization of proton conducting ceramics for developing hydrogen separation membranes.
- Synthesis, processing, and characterization of composites of metal/proton conducting ceramic and electronic conducting ceramic/proton conducting ceramic for developing hydrogen separation membranes.
- Investigation of the sintering of dense membranes on porous substrates.
- Testing of hydrogen permeation of the membranes.
Introduction
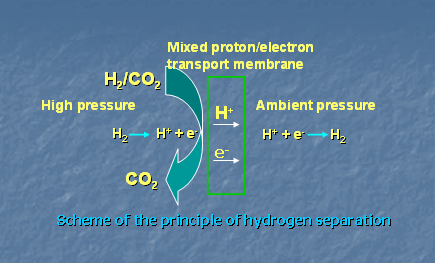
As shown in the schematic of hydrogen separation, hydrogen separation membranes are mixed proton and electron conducting materials that can separate hydrogen from other gases, thereby, obtain high purity hydrogen. The membranes play an important role in the production of hydrogen. For example, one of the objectives of the FutureGen project (a 1 billion US$, 10 year project) is to produce hydrogen from coal and to sequestrate CO2. In the FutureGen project, as shown in the following schematic, hydrogen separation membranes are needed to separate hydrogen from high-temperature, high pressure mixed gases (mainly H2 and CO2). The present work is to develop hydrogen separation membranes that have high hydrogen permeation and can withstand high temperature and pressure.

Approach, Facilities and Capabilities
- Proton conducting ceramics are fabricated and characterized using the methods and facilities described in our website of SOFC research.
- In order to increase the electronic conductivity in the proton conducting ceramics, composites (including powders, bulks, and membranes) of metal/proton conducting ceramic and electronic conducting ceramic/proton conducting ceramic are fabricated and characterized using the methods and facilities described in our website of SOFC research.
- Hydrogen permeation of the samples at high temperatures up to 1000°C is tested in our home-built testing system with an Agilent 6890N gas Chromatograph.
Updated: April 11, 2013 14:33
